Understanding OSHA Negligence: Duty, Breach, and Harm in Workplace Safety
Workplace safety is critical, and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a significant role in regulating and enforcing safety standards. Employers are required to maintain a safe work environment, but when they fail to meet these standards, it can lead to serious accidents and injuries. This article explores OSHA negligence, breaking down the key elements—duty, breach, and harm— and examining what they mean for both employees and employers. Understanding these concepts is essential for ensuring workplace accountability and reducing safety risks.
In this context, OSHA negligence refers to an employer’s failure to comply with OSHA regulations, which can result in harm to employees. In legal terms, proving negligence involves showing that the employer had a duty to provide a safe workplace, breached that duty, and caused harm as a result. Let’s dive into these elements more closely.
1. The Duty of Care Under OSHA
Every employer in the United States has a duty to provide a safe and healthy workplace under the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970. This duty involves several key responsibilities, including:
- Maintaining a hazard-free environment: Employers must identify and mitigate risks such as toxic chemicals, dangerous machinery, or unsafe working conditions.
- Following OSHA standards: OSHA has developed specific guidelines and regulations that apply to different industries. Employers are required to comply with these standards.
- Providing adequate training: Workers should be properly trained in how to safely perform their tasks and use equipment.
- Reporting and recordkeeping: Employers must report serious injuries and fatalities to OSHA and keep records of workplace injuries.
By law, failing to meet these duties can be considered negligence. The duty of care is a foundational element in determining whether an employer is legally responsible for an injury or death in the workplace.
Legal Framework and Employer Responsibilities
OSHA compliance is mandatory, and failure to comply can lead to severe penalties. The legal framework is designed to protect workers, but the employer’s negligence in maintaining this standard can open them up to liability. When a worker files a complaint, OSHA inspectors may investigate to determine if the employer violated safety standards.
Case Study: Construction Site Hazards
Consider a construction site where heavy machinery is in use. Employers must ensure that workers are trained to operate the equipment safely and provide proper protective gear. If an employer fails to do so, and a worker is injured as a result, the employer may be found negligent for not fulfilling their duty of care.
2. Breach of Duty: What Constitutes OSHA Negligence?
A breach of duty occurs when an employer fails to meet their legal obligations under OSHA guidelines. This could involve ignoring safety regulations, not providing necessary safety gear, or failing to train employees adequately.
Common examples of breaches include:
- Failure to implement safety protocols: Skipping critical safety steps, like providing personal protective equipment (PPE) in hazardous environments.
- Ignoring maintenance needs: Not properly maintaining equipment or failing to replace faulty machinery.
- Inadequate hazard communication: Not informing employees about dangerous substances or practices that could harm them.
When these or similar failures occur, and someone is injured, it can constitute OSHA negligence. The burden of proof often falls on the injured worker to demonstrate that the employer breached their duty, leading to the accident.
External Links to Breach Examples
For example, OSHA provides detailed safety standards that employers must adhere to. Employers can face penalties for non-compliance with these standards, as shown in this official OSHA guideline on hazard communication OSHA Hazard Communication Standard.
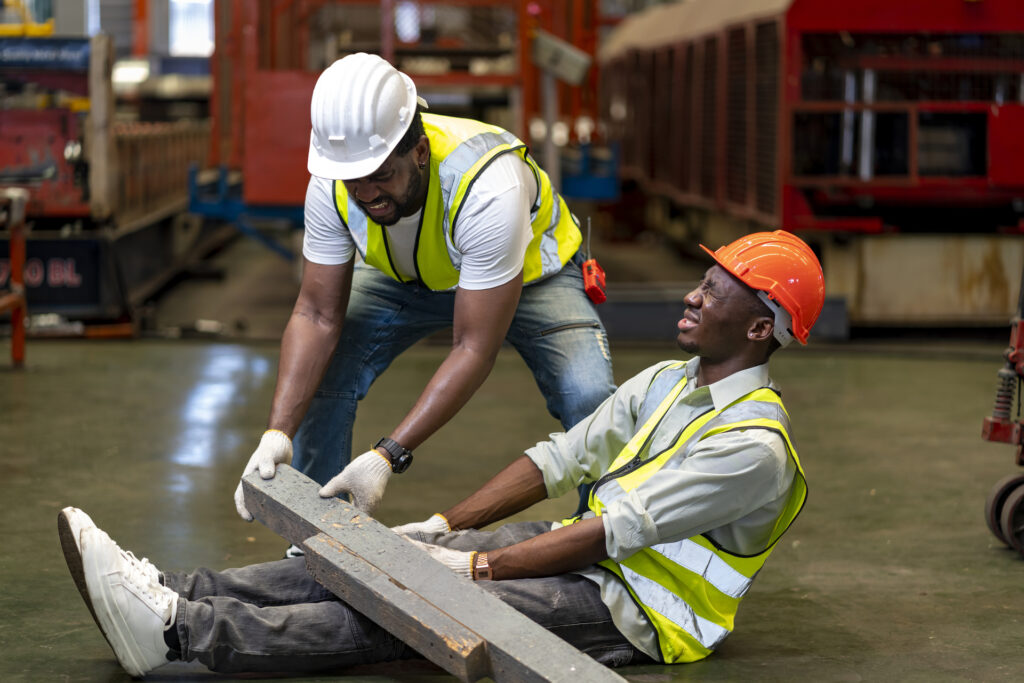

3. Harm: The Consequences of Negligence
The final element in proving OSHA negligence is demonstrating that the breach of duty caused harm to an employee. Harm can take many forms, including:
- Physical injuries: From minor cuts and bruises to severe injuries like amputations, fractures, or even death.
- Psychological harm: Stress and trauma can also be significant consequences, especially after a major workplace accident.
- Financial harm: Medical expenses, lost wages, and long-term disability can have lasting financial effects on workers and their families.
In many cases, an injured worker may seek compensation through workers’ compensation claims. However, in situations where OSHA negligence is proven, employers can face additional legal liabilities.
Real-World Example: Manufacturing Accident
In a real-world case, a worker at a manufacturing plant suffered severe burns due to a malfunctioning machine. The machine had not been properly maintained, and safety checks were ignored. The employer was found negligent under OSHA guidelines, leading to hefty fines and a personal injury lawsuit. This case highlights how breaches of OSHA standards can directly result in harm, and how proving negligence is critical for obtaining justice.
4. OSHA Penalties and Employer Accountability
When negligence is established, employers can face significant legal and financial penalties. OSHA has the authority to issue fines, require corrective actions, and in some cases, shut down operations. Penalties can range from minor fines to large sums depending on the severity of the breach and the harm caused.
Key Factors Influencing Penalties:
- Severity of the violation: Serious breaches involving fatalities or multiple injuries often result in higher fines.
- Repeat offenses: Employers with a history of non-compliance face harsher penalties.
- Willful violations: If an employer knowingly disregards OSHA regulations, they may face both civil and criminal penalties.
Moreover, civil lawsuits filed by injured employees can lead to additional financial settlements and damages. Employers who prioritize safety and comply with OSHA standards can reduce their risks of facing negligence claims and improve overall workplace safety.
FAQ Section
1. What is considered OSHA negligence?
OSHA negligence occurs when an employer fails to follow OSHA’s safety regulations, resulting in harm to employees. It typically involves proving that the employer had a duty of care, breached that duty, and caused harm.
2. How can an employee prove an employer was negligent under OSHA?
An employee must show that the employer violated OSHA standards, leading to an unsafe work environment, and that this breach directly caused the employee’s injury or illness.
3. What penalties can employers face for OSHA violations?
Penalties range from fines to operational shutdowns, depending on the severity of the violation. Serious offenses, repeat violations, or willful negligence can result in steep penalties and legal liabilities.
4. Can OSHA negligence lead to criminal charges?
Yes, in cases of willful negligence where an employer knowingly disregards safety standards, criminal charges may be pursued.
5. How can employers avoid OSHA negligence claims?
Employers should ensure strict compliance with OSHA standards, provide regular training, maintain safety equipment, and address hazards promptly to minimize risks.
6. Is workers’ compensation affected by OSHA negligence?
Workers’ compensation typically covers workplace injuries, but in cases of proven negligence, employers may face additional lawsuits and financial penalties beyond standard compensation claims.
Key Takeaways
- OSHA requires employers to provide safe workplaces, and negligence can result in serious harm to employees.
- Negligence involves proving duty, breach, and harm, with penalties ranging from fines to criminal charges.
- Regular compliance with OSHA standards can prevent workplace injuries and reduce legal liabilities for employers.
Read More: What Does a Hearing in Court Mean?