Civil liberties form the backbone of modern democratic societies, ensuring that individuals are protected from undue government interference in their personal lives. These liberties, often enshrined in constitutions and legal frameworks, are essential for upholding human rights and freedoms. But when asked, which statement best defines the term civil liberties, the answer lies in understanding the delicate balance between individual freedoms and government authority.
This article explores the concept of civil liberties, their significance in democratic societies, and how they are protected by law. Through a deep dive into the historical evolution of civil liberties and their present-day importance, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how these rights impact everyday life.
Understanding Civil Liberties: A Foundational Concept
At its core, civil liberties refer to the basic freedoms guaranteed to individuals, protecting them from excessive government power. These liberties are usually found in constitutional documents like the U.S. Bill of Rights or international agreements like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
But which statement best defines the term civil liberties? Civil liberties can be defined as the rights and freedoms that protect individuals from government overreach, ensuring that personal freedoms like speech, privacy, and freedom of religion remain intact.
While these liberties exist globally, they vary in scope and enforcement depending on the country’s legal and political system. For example, in the United States, civil liberties include the right to free speech, freedom of assembly, and protection from unreasonable searches and seizures. In contrast, other countries may limit some of these rights depending on their political structure and laws.
Key Civil Liberties Protected by Law
Civil liberties span a wide range of personal freedoms, but some of the most universally recognized include:
- Freedom of Speech and Expression
The right to express one’s opinions without fear of government censorship is one of the most fundamental civil liberties. This freedom allows individuals to speak freely, protest, and share ideas, even if they criticize the government. - Right to Privacy
Privacy is another key aspect of civil liberties. Governments are restricted from intruding into personal matters, such as the privacy of one’s home, communication, and personal data. For example, protections against unreasonable searches and seizures ensure that law enforcement agencies cannot conduct invasive searches without due cause. - Freedom of Religion
The right to practice or not practice a religion of one’s choosing is essential in maintaining the separation of church and state. Individuals are free to observe their faith without interference or coercion by the government. - Right to a Fair Trial
Legal systems around the world enshrine the right to a fair and impartial trial. This ensures that individuals accused of crimes are given a fair hearing, with the opportunity to defend themselves in court. It also guards against arbitrary arrests and detentions. - Freedom of Assembly and Association
The right to peacefully gather and protest is a hallmark of democratic societies. Civil liberties ensure that citizens can assemble, form groups, and express collective views, whether for social, political, or cultural purposes.
Each of these liberties is designed to protect individuals from government overreach, allowing citizens to engage freely in democratic processes without fear of retaliation or oppression.
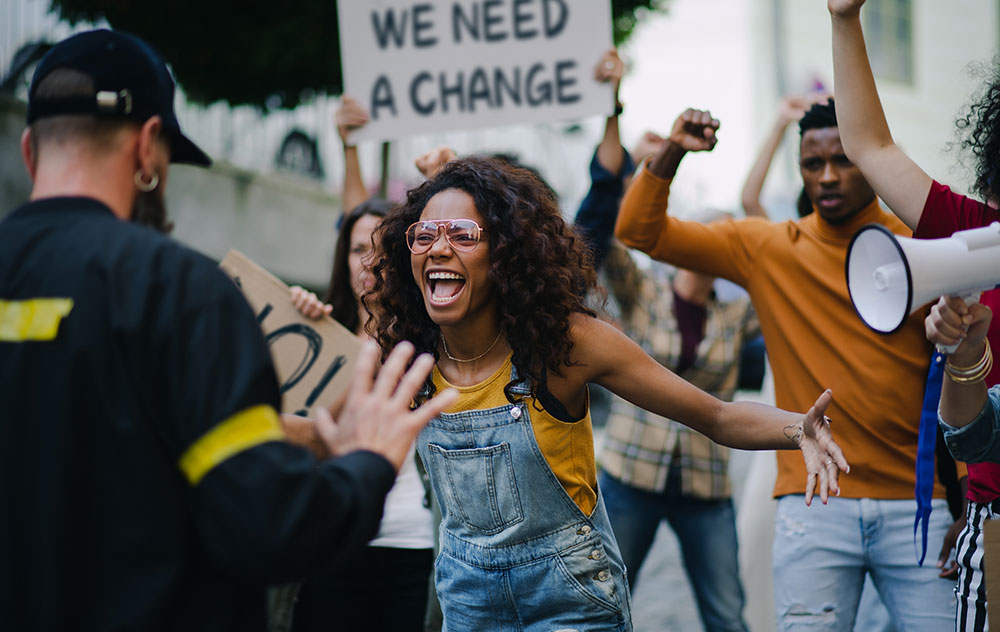
Civil Liberties vs. Civil Rights: Understanding the Distinction
Although often used interchangeably, civil liberties and civil rights differ in their focus. Civil liberties primarily refer to protections from government actions, while civil rights focus on equal treatment under the law. In essence, civil liberties protect individual freedoms, while civil rights ensure that these freedoms are equally applied to all individuals, regardless of race, gender, or other characteristics.
For example, while the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution protects free speech (a civil liberty), civil rights laws, like the Civil Rights Act of 1964, ensure that individuals are not discriminated against in public spaces, employment, or education based on race or gender.
Both civil liberties and civil rights are crucial for the functioning of a just society, and they often work hand in hand to prevent both government overreach and societal discrimination.
Which Statement Best Defines the Term Civil Liberties? Exploring Real-World Examples
To answer which statement best defines the term civil liberties, let’s examine a few real-world scenarios:
- Edward Snowden and the Right to Privacy
In 2013, Edward Snowden exposed the extent of the U.S. government’s surveillance programs, revealing how mass data collection by the National Security Agency (NSA) infringed on citizens’ privacy rights. This case raised concerns about the balance between national security and individual privacy—both critical civil liberties issues. - Freedom of Speech: Protests and Government Repression
Across the world, freedom of speech is often tested through protests. For instance, during the Arab Spring uprisings, citizens demanded reforms in several Middle Eastern countries. In some cases, governments responded with force, limiting the people’s ability to protest peacefully—highlighting the ongoing struggle to protect civil liberties under authoritarian regimes. - Same-Sex Marriage and Civil Liberties
The legalization of same-sex marriage in the United States in 2015 exemplified the intersection of civil liberties and civil rights. The right to marry, which falls under personal freedom, was extended to all citizens, reflecting a broader understanding of civil liberties in a modern context.
The Role of the Judiciary in Protecting Civil Liberties
Civil liberties are often upheld or contested in courts, where judges interpret constitutional provisions to determine the extent of these freedoms. For instance, the U.S. Supreme Court has played a crucial role in shaping civil liberties through landmark cases like Roe v. Wade (1973), which recognized a woman’s right to privacy in making reproductive choices, and Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which ended racial segregation in public schools.
The judiciary acts as a check on government power, ensuring that laws and policies do not infringe on the basic freedoms guaranteed to individuals. In many countries, constitutional courts play a similar role, acting as arbiters between the state and its citizens.
FAQs on Civil Liberties
Civil liberties refer to specific freedoms protected by law within a country, while human rights are universal and inherent to all individuals regardless of their legal system. Human rights are broader, encompassing rights like the right to life and education, whereas civil liberties often focus on protecting individuals from government interference.
Civil liberties are primarily protected through constitutional frameworks, legal precedents, and judicial interpretation. Courts play a crucial role in ensuring that these rights are upheld and that governments do not overstep their boundaries.
Yes, civil liberties can be limited under certain circumstances, such as in times of national emergency or war. However, such limitations must be justified and proportionate to the situation, ensuring that the government does not use these situations as a pretext to curtail freedoms unnecessarily.
Civil liberties laws vary depending on the country’s constitution and legal system. While democratic nations tend to have stronger protections for civil liberties, authoritarian regimes may impose more restrictions.
Yes, civil liberties can evolve, as societal norms and judicial interpretations change. Courts may expand or contract certain liberties based on legal challenges and shifting public opinions.
Key Takeaways
- Civil liberties protect individual freedoms from government overreach.
- These liberties include the right to free speech, privacy, religion, and assembly.
- Courts play a key role in interpreting and enforcing civil liberties.
- Civil liberties differ from civil rights, focusing on individual freedoms rather than equal treatment.
Read More: Which Article Proclaims the Constitution as the Highest Law?
- American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU)
ACLU, Amerika Birleşik Devletleri’ndeki en büyük sivil özgürlük savunucularından biridir. Onların çalışmaları, sivil özgürlüklerin korunmasına yönelik çeşitli hukuki mücadeleleri içerir.
ACLU Official Website - U.S. Constitution (Bill of Rights)
Amerika Birleşik Devletleri Anayasası’nın Haklar Bildirgesi, ülkedeki temel sivil özgürlüklerin dayandığı yasal metindir. Bu belge, özgürlüklerin korunması için anayasal bir çerçeve sağlar.
Bill of Rights – U.S. National Archives - United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
Evrensel İnsan Hakları Beyannamesi, dünya genelinde temel insan haklarını ve özgürlüklerini garanti altına almak için oluşturulmuş uluslararası bir belgedir.
UDHR – United Nations

Jonathan Hartley is a highly regarded senior criminal lawyer with over 15 years of experience in the UK legal system. He began his career at a prestigious law firm in London, where he specialized in both defense and criminal law. Known for his ability to craft compelling defense strategies, Jonathan has successfully represented clients in high-profile cases and earned multiple awards for his contributions to the field of law.
In addition to his legal practice, Jonathan is also an accomplished legal writer, contributing articles to top legal blogs and online platforms. His work not only provides valuable insights into legal matters but also meets Google’s E-E-A-T standards by delivering accurate, reliable, and trustworthy information to readers. Committed to legal ethics and public welfare, Jonathan actively participates in discussions on law and justice while educating the public through his writing.










